If you have observed a suspicious lesion, you may be wondering: Do I have melanoma?
This is especially true if the growth exhibits signs of asymmetry, irregular borders, multiple colors, diameter greater than the size of a pencil eraser, or changing appearance.
Continue reading to learn all about melanoma detection and diagnosis.
What Is Melanoma?
Melanoma is a type of skin cancer that originates in melanocytes (cells that produce pigment) and occurs when these cells grow out of control.
It often presents as a new or existing mole that’s changed in size, shape, color, and/or elevation.
While melanoma is less common than other types of skin cancer, such as basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma, it is more likely to metastasize, which makes it far deadlier.
Do I Have Melanoma?
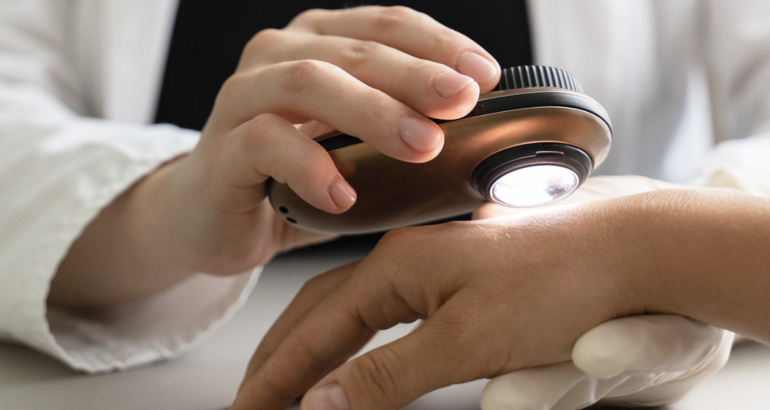
Do I have melanoma? A board-certified dermatologist who specializes in skin cancer is best-qualified to answer this question.
In order to diagnose melanoma, the doctor will conduct a thorough medical history and perform a head-to-toe skin cancer screening.
If he notes any suspicious lesions, they will be biopsied and sent to the lab to confirm melanoma.
Additional Testing
Upon receiving a melanoma diagnosis, a skin cancer specialist may recommend additional tests to determine if and where the cancer has spread:
- Chest x-ray – used to determine if melanoma has metastasized to the lungs
- Ultrasound – employs sound waves to visualize the body and can see if cancer has spread to nearby lymph nodes
- CT scan – helps detect spread to lymph nodes and other organs and can also be used to guide a needle for biopsy
- MRI scan – uses radio waves and powerful magnets to visualize areas inside the body such as the brain and spinal cord and can determine if melanoma has metastasized to these areas
Learn More About Melanoma
If you have detected a suspicious lesion and are concerned that it may be melanoma, please call our office today to schedule a comprehensive consultation with board-certified dermatologist and fellowship-trained Mohs surgeon Dr. Johnathan L. Chappell.